Journal Archive
2022
Day 76: Solving one of LeetCode problems
257. Binary Tree Paths Difficulty - Easy
Given the root of a binary tree, return all root-to-leaf paths in any order.
A leaf is a node with no children.
Example 1:
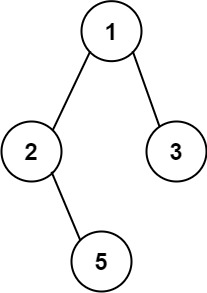
Input: root = [1,2,3,null,5] Output: ["1->2->5","1->3"]
Example 2:
Input: root = [1] Output: ["1"]